Using Gradio and Comet
Tags: COMET, SPACES Contributed by the Comet team
Introduction
In this guide we will demonstrate some of the ways you can use Gradio with Comet. We will cover the basics of using Comet with Gradio and show you some of the ways that you can leverage Gradio’s advanced features such as Embedding with iFrames and State to build some amazing model evaluation workflows.
Here is a list of the topics covered in this guide.
- Logging Gradio UI’s to your Comet Experiments
- Embedding Gradio Applications directly into your Comet Projects
- Embedding Hugging Face Spaces directly into your Comet Projects
- Logging Model Inferences from your Gradio Application to Comet
What is Comet?
Comet is an MLOps Platform that is designed to help Data Scientists and Teams build better models faster! Comet provides tooling to Track, Explain, Manage, and Monitor your models in a single place! It works with Jupyter Notebooks and Scripts and most importantly it’s 100% free!
Setup
First, install the dependencies needed to run these examples
pip install comet_ml torch torchvision transformers gradio shap requests PillowNext, you will need to sign up for a Comet Account. Once you have your account set up, grab your API Key and configure your Comet credentials
If you’re running these examples as a script, you can either export your credentials as environment variables
export COMET_API_KEY="<Your API Key>"
export COMET_WORKSPACE="<Your Workspace Name>"
export COMET_PROJECT_NAME="<Your Project Name>"or set them in a .comet.config file in your working directory. You file should be formatted in the following way.
[comet]
api_key=<Your API Key>
workspace=<Your Workspace Name>
project_name=<Your Project Name>If you are using the provided Colab Notebooks to run these examples, please run the cell with the following snippet before starting the Gradio UI. Running this cell allows you to interactively add your API key to the notebook.
import comet_ml
comet_ml.init()1. Logging Gradio UI’s to your Comet Experiments
In this example, we will go over how to log your Gradio Applications to Comet and interact with them using the Gradio Custom Panel.
Let’s start by building a simple Image Classification example using resnet18.
import comet_ml
import requests
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
torch.hub.download_url_to_file("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/images/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg")
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda"
else:
device = "cpu"
model = torch.hub.load("pytorch/vision:v0.6.0", "resnet18", pretrained=True).eval()
model = model.to(device)
# Download human-readable labels for ImageNet.
response = requests.get("https://git.io/JJkYN")
labels = response.text.split("\n")
def predict(inp):
inp = Image.fromarray(inp.astype("uint8"), "RGB")
inp = transforms.ToTensor()(inp).unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
prediction = torch.nn.functional.softmax(model(inp.to(device))[0], dim=0)
return {labels[i]: float(prediction[i]) for i in range(1000)}
inputs = gr.Image()
outputs = gr.Label(num_top_classes=3)
io = gr.Interface(
fn=predict, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, examples=["dog.jpg"]
)
io.launch(inline=False, share=True)
experiment = comet_ml.Experiment()
experiment.add_tag("image-classifier")
io.integrate(comet_ml=experiment)The last line in this snippet will log the URL of the Gradio Application to your Comet Experiment. You can find the URL in the Text Tab of your Experiment.
Add the Gradio Panel to your Experiment to interact with your application.
2. Embedding Gradio Applications directly into your Comet Projects
If you are permanently hosting your Gradio application, you can embed the UI using the Gradio Panel Extended custom Panel.
Go to your Comet Project page, and head over to the Panels tab. Click the + Add button to bring up the Panels search page.
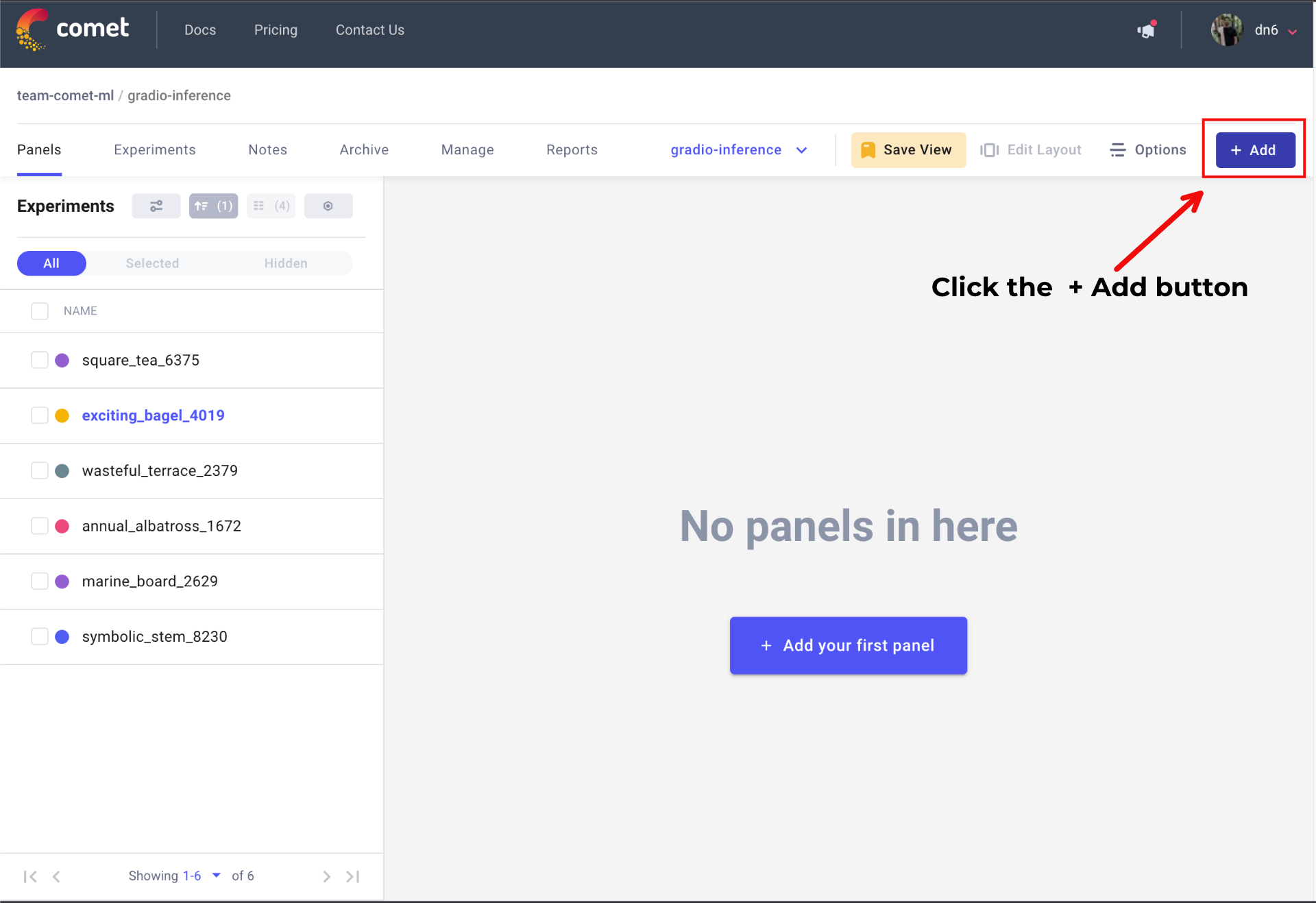
Next, search for Gradio Panel Extended in the Public Panels section and click Add.
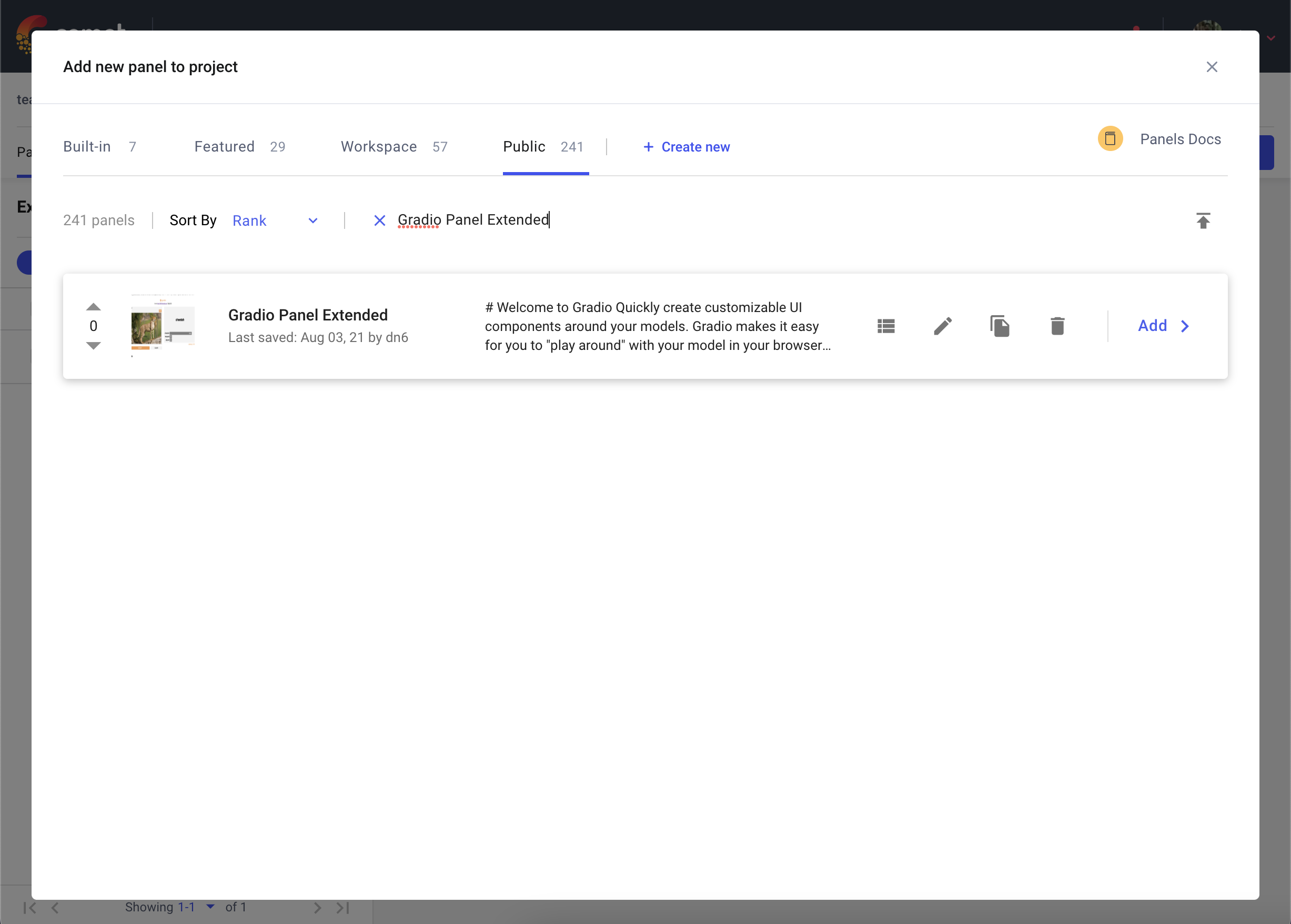
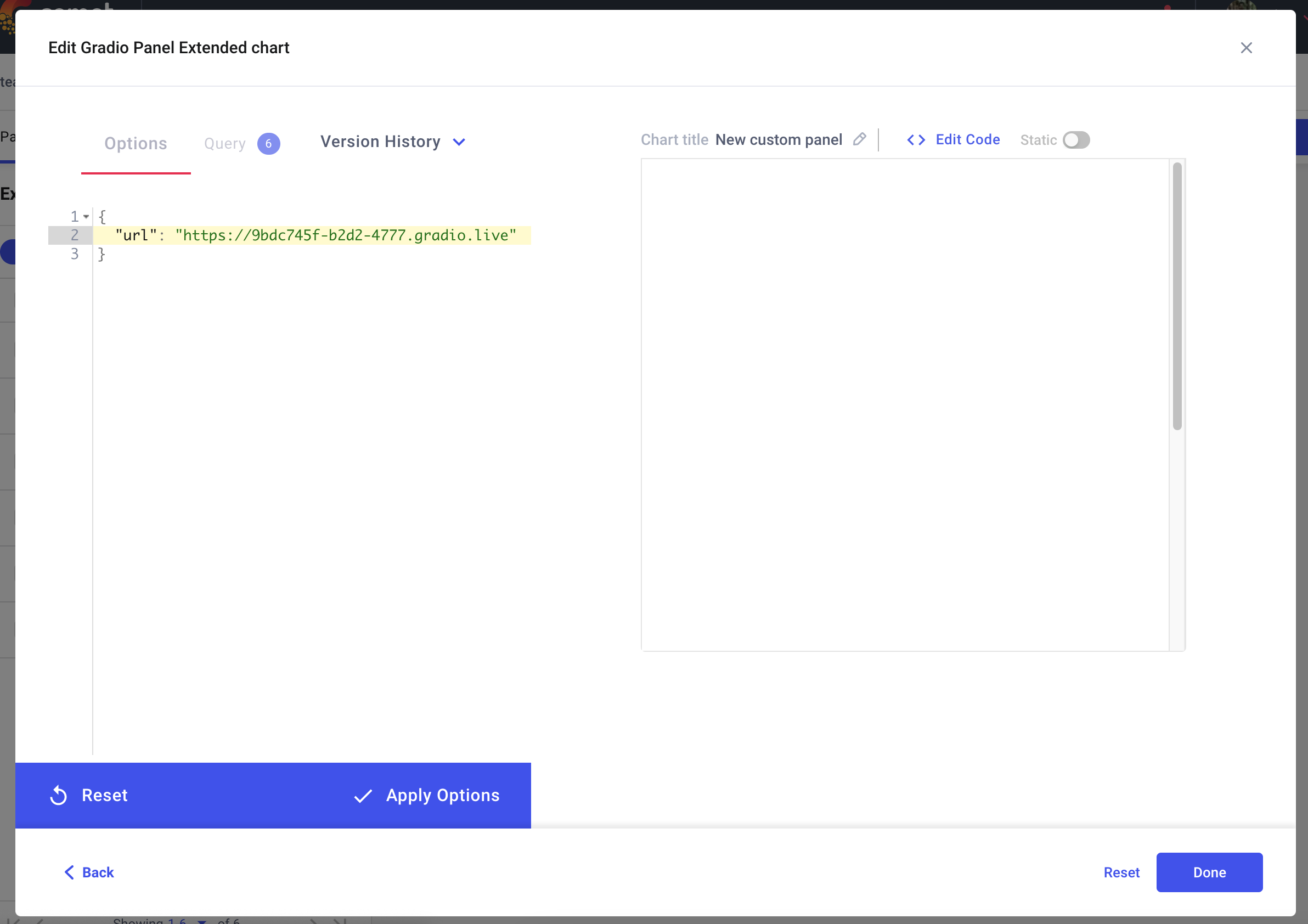
Once you have added your Panel, click Edit to access to the Panel Options page and paste in the URL of your Gradio application.
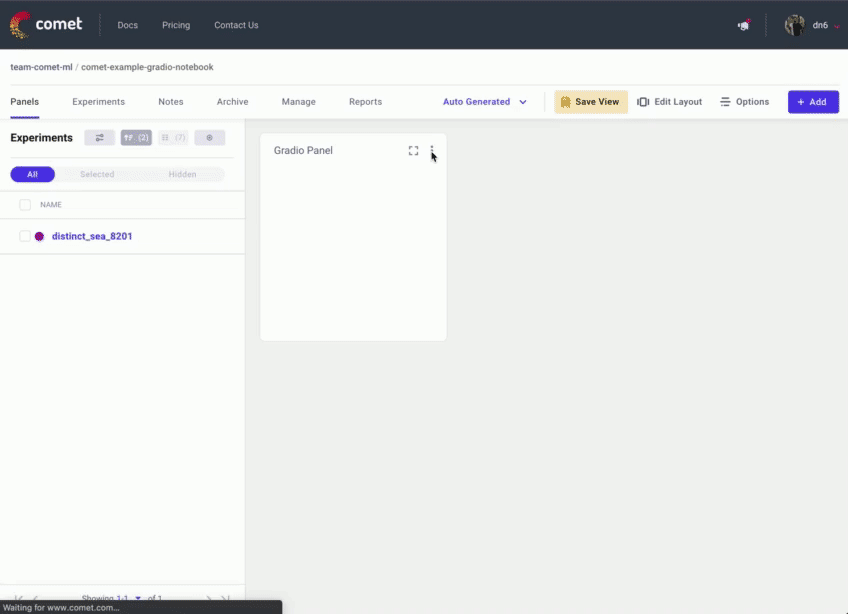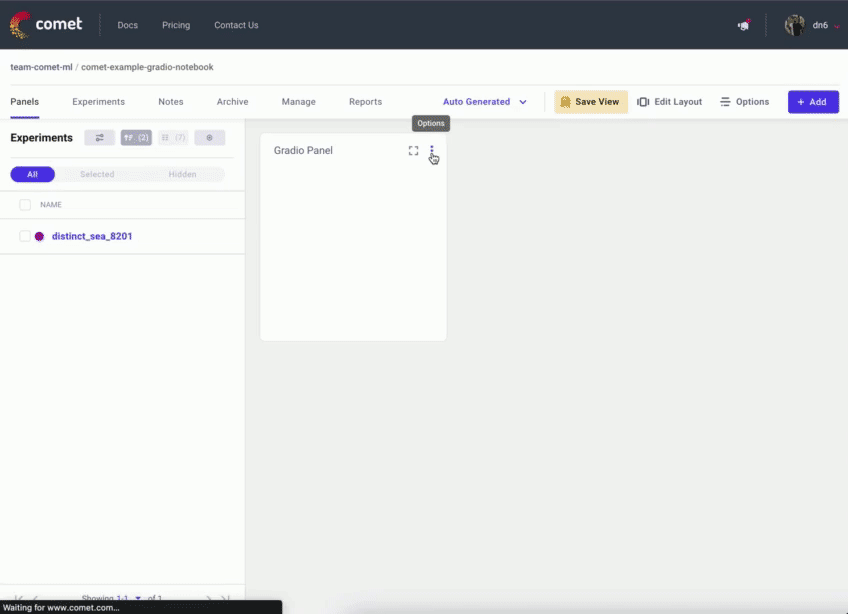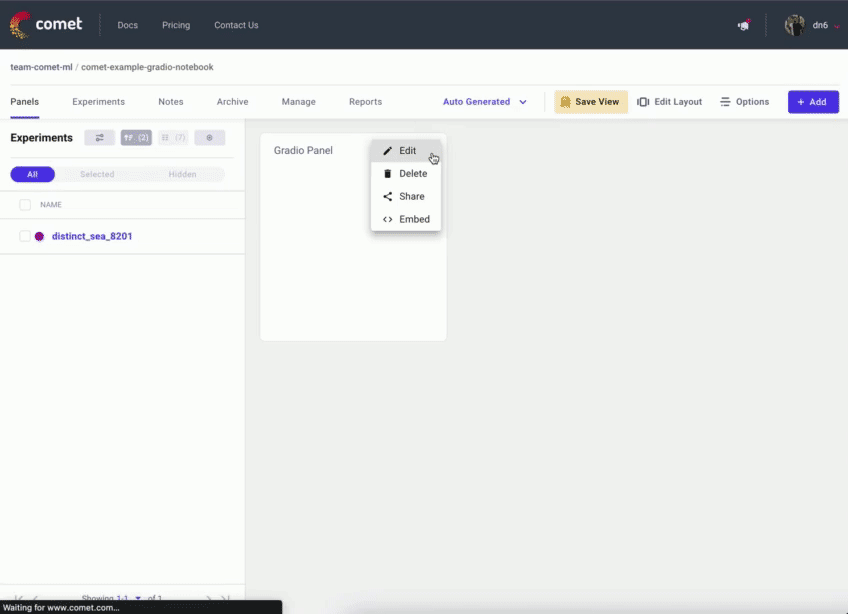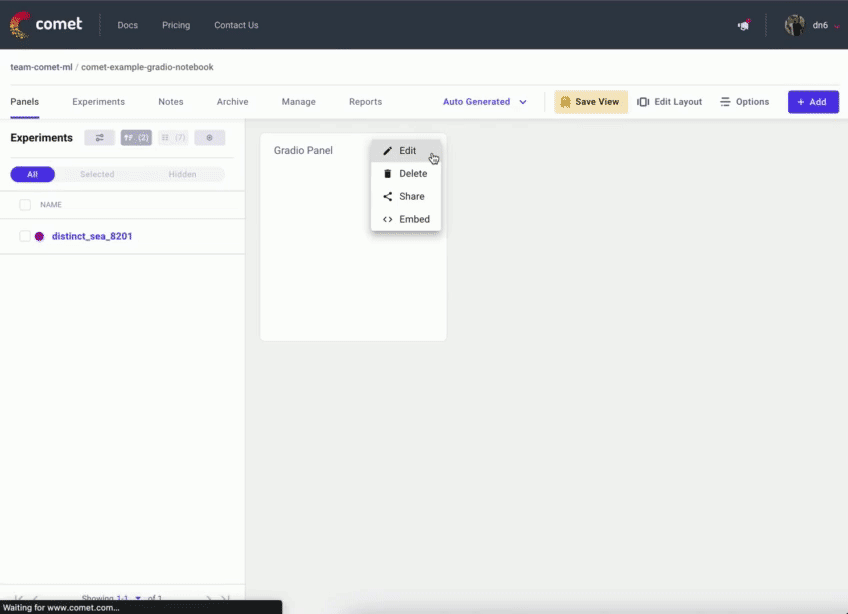
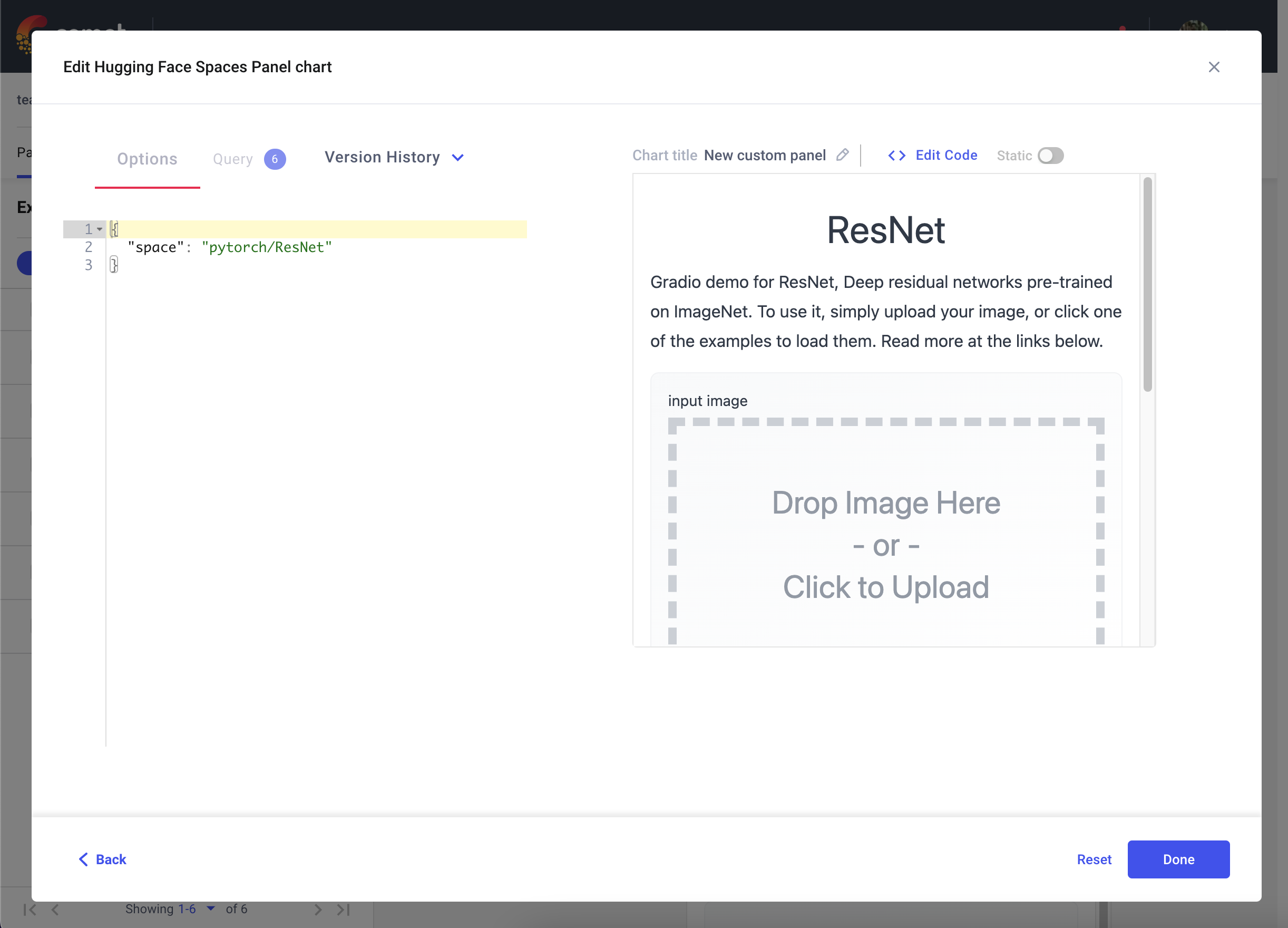
3. Embedding Hugging Face Spaces directly into your Comet Projects
You can also embed Gradio Applications that are hosted on Hugging Faces Spaces into your Comet Projects using the Hugging Face Spaces Panel.
Go to your Comet Project page, and head over to the Panels tab. Click the + Add button to bring up the Panels search page. Next, search for the Hugging Face Spaces Panel in the Public Panels section and click Add.
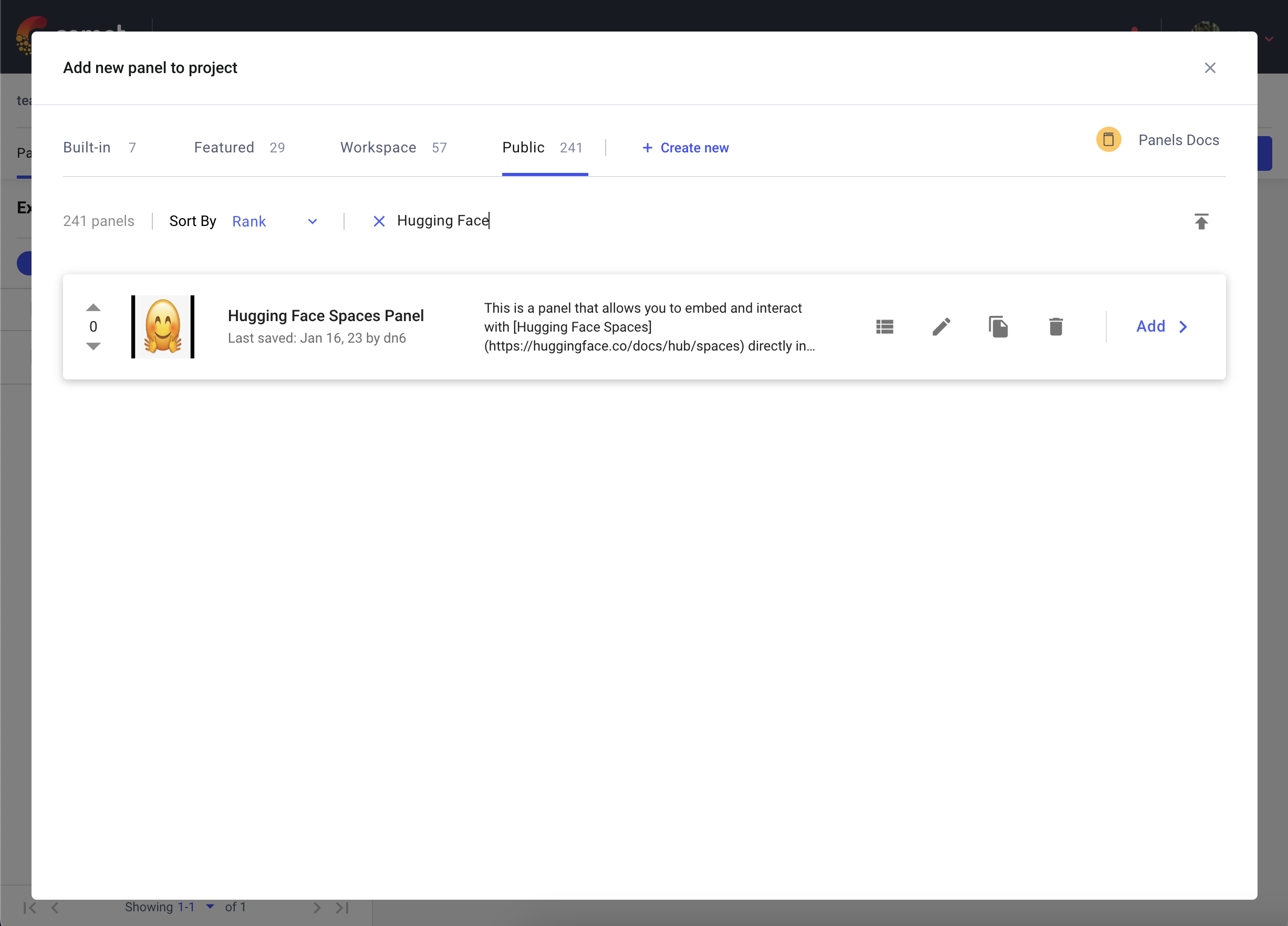
Once you have added your Panel, click Edit to access to the Panel Options page and paste in the path of your Hugging Face Space e.g. pytorch/ResNet
4. Logging Model Inferences to Comet
In the previous examples, we demonstrated the various ways in which you can interact with a Gradio application through the Comet UI. Additionally, you can also log model inferences, such as SHAP plots, from your Gradio application to Comet.
In the following snippet, we’re going to log inferences from a Text Generation model. We can persist an Experiment across multiple inference calls using Gradio’s State object. This will allow you to log multiple inferences from a model to a single Experiment.
import comet_ml
import gradio as gr
import shap
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda"
else:
device = "cpu"
MODEL_NAME = "gpt2"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME)
# set model decoder to true
model.config.is_decoder = True
# set text-generation params under task_specific_params
model.config.task_specific_params["text-generation"] = {
"do_sample": True,
"max_length": 50,
"temperature": 0.7,
"top_k": 50,
"no_repeat_ngram_size": 2,
}
model = model.to(device)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME)
explainer = shap.Explainer(model, tokenizer)
def start_experiment():
"""Returns an APIExperiment object that is thread safe
and can be used to log inferences to a single Experiment
"""
try:
api = comet_ml.API()
workspace = api.get_default_workspace()
project_name = comet_ml.config.get_config()["comet.project_name"]
experiment = comet_ml.APIExperiment(
workspace=workspace, project_name=project_name
)
experiment.log_other("Created from", "gradio-inference")
message = f"Started Experiment: [{experiment.name}]({experiment.url})"
return (experiment, message)
except Exception as e:
return None, None
def predict(text, state, message):
experiment = state
shap_values = explainer([text])
plot = shap.plots.text(shap_values, display=False)
if experiment is not None:
experiment.log_other("message", message)
experiment.log_html(plot)
return plot
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
start_experiment_btn = gr.Button("Start New Experiment")
experiment_status = gr.Markdown()
# Log a message to the Experiment to provide more context
experiment_message = gr.Textbox(label="Experiment Message")
experiment = gr.State()
input_text = gr.Textbox(label="Input Text", lines=5, interactive=True)
submit_btn = gr.Button("Submit")
output = gr.HTML(interactive=True)
start_experiment_btn.click(
start_experiment, outputs=[experiment, experiment_status]
)
submit_btn.click(
predict, inputs=[input_text, experiment, experiment_message], outputs=[output]
)Inferences from this snippet will be saved in the HTML tab of your experiment.
Conclusion
We hope you found this guide useful and that it provides some inspiration to help you build awesome model evaluation workflows with Comet and Gradio.
How to contribute Gradio demos on HF spaces on the Comet organization
- Create an account on Hugging Face here.
- Add Gradio Demo under your username, see this course for setting up Gradio Demo on Hugging Face.
- Request to join the Comet organization here.